Understanding the four stages of the real estate market cycle is crucial for investors looking to navigate the complexities of real estate investing effectively. Each stage presents unique opportunities and challenges, and recognizing these stages can help you make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding properties. Here’s a detailed overview of the four stages of the real estate market cycle and how to identify them.
4 Stages Of The Real Estate Market Cycle:
Analyzing Economic Indicators
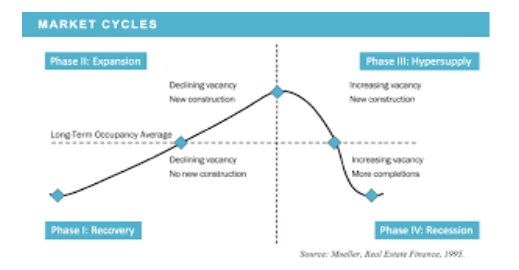
1. Recovery Stage
The recovery stage marks the beginning of the real estate cycle, typically following a recession. During this phase, the market starts to stabilize after a downturn, and several key indicators signal the onset of recovery:
- Increasing Demand: As the economy begins to recover, demand for properties starts to rise. Investors will notice that property values stop declining and begin to stabilize or increase.
- Low Inventory Levels: There may still be a surplus of properties from the previous downturn, but buyers begin to show interest, leading to a gradual absorption of available inventory.
- Rising Rental Rates: As demand increases, rental rates may start to rise, indicating a healthier rental market.
Investors should look for signs of increased buyer activity, such as more inquiries on listings and shorter times on the market. This stage is often characterized by opportunities to purchase undervalued properties, making it an ideal time for savvy investors to enter the market.
2. Expansion Stage
The expansion stage is characterized by significant growth in the real estate market. This phase occurs when economic conditions improve, leading to increased demand for housing and commercial properties. Key indicators include:
- High Employment Rates: Job growth is robust, contributing to higher disposable incomes and increased consumer confidence. This often leads to more people looking to buy or rent homes.
- Rising Property Values: Property prices begin to rise rapidly due to increased demand and limited supply. Investors may notice bidding wars for desirable properties.
- Increased Construction Activity: Developers respond to demand by starting new construction projects, further enhancing market activity.
During this stage, investors should consider strategies such as quick flips, rental investments, and development projects to capitalize on the growing market. However, competition can be fierce, so thorough market analysis is essential.
3. Hyper-Supply Stage
The hyper-supply stage occurs when the market becomes oversaturated with properties. This phase can be tricky, as it often follows a period of rapid expansion. Key indicators of hyper-supply include:
- Excess Inventory: The supply of properties exceeds demand, leading to longer listing times and increased competition among sellers.
- Stabilizing or Declining Prices: Property values may begin to plateau or decline as buyers have more options and can negotiate better deals.
- High Vacancy Rates: Rental properties may experience higher vacancy rates as tenants have more choices, leading to increased pressure on rental prices.
Investors should be cautious during this stage, focusing on value-buying opportunities and stabilizing existing rental properties. It’s also a good time to diversify investments beyond traditional residential properties to mitigate risks associated with oversupply.
4. Recession Stage
The recession stage is the final phase of the real estate cycle, characterized by a significant downturn in the market. This stage is marked by:
- Declining Property Values: Home prices drop significantly as demand wanes, and many properties may sell for less than their asking prices.
- High Vacancy Rates: Rental demand decreases, leading to higher vacancy rates and lower rental income for property owners.
- Increased Foreclosures: Economic challenges may force some homeowners into foreclosure, presenting potential buying opportunities for investors willing to take risks.
While the recession stage can be challenging, it also offers opportunities for investors to acquire distressed properties at lower prices. Those who can identify potential bargains during this phase may find significant rewards when the market eventually recovers.
Identifying the Stages of the Real Estate Cycle
To accurately identify the current stage of the real estate market cycle, investors should analyze various factors, including:
- Market Data: Monitor property prices, sales volumes, and rental rates to gauge market activity.
- Economic Indicators: Stay informed about employment rates, GDP growth, and consumer confidence, as these factors influence real estate demand.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: Observe inventory levels and absorption rates to determine whether the market is tightening or loosening.
- Expert Opinions: Consult with local real estate professionals to gain insights into market conditions and trends.
Understanding the cyclical nature of real estate allows investors to make strategic decisions that align with market conditions. By recognizing the signs of each phase, investors can better position themselves to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Conclusion
Navigating the real estate market cycle requires a keen understanding of its four stages: recovery, expansion, hyper-supply, and recession. By closely monitoring economic indicators and market data, investors can identify these stages and make informed decisions that align with their investment strategies.
Are you ready to leverage the insights of the real estate market cycle for your investment strategy? Contact us today to learn more about how to identify emerging opportunities in the real estate market!
FAQs
- What are the four stages of the real estate market cycle?
The four stages are recovery, expansion, hyper-supply, and recession.
- How long do real estate market cycles typically last?
Real estate market cycles usually last between 10 to 18 years, but the duration of each stage can vary based on economic and social factors.
- What indicators signal the start of the recovery stage?
Indicators include increasing demand, stabilizing property values, and rising rental rates.
- How can I identify the hyper-supply stage?
Look for excess inventory, stabilizing or declining prices, and high vacancy rates.
- What investment strategies are effective during a recession?
Investors can focus on acquiring distressed properties, holding onto existing rentals, or looking for undervalued assets with potential for appreciation.
Introduction to Multifamily Real Estate Syndication
Welcome to the exciting world of multifamily real estate syndication, a realm where collaboration, strategy, and smart investing converge to create remarkable opportunities for investors like you. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, this guide will illuminate the path to potentially lucrative and wise investments in real estate syndication.
Real Estate Syndication
Why Consider Multifamily Real Estate Syndication?
Imagine having the key to unlock larger, more lucrative real estate deals that were previously out of reach. Multifamily real estate syndication does exactly that. By pooling resources with other investors, you gain access to significant commercial real estate opportunities, tapping into markets that promise higher returns and greater growth potential.
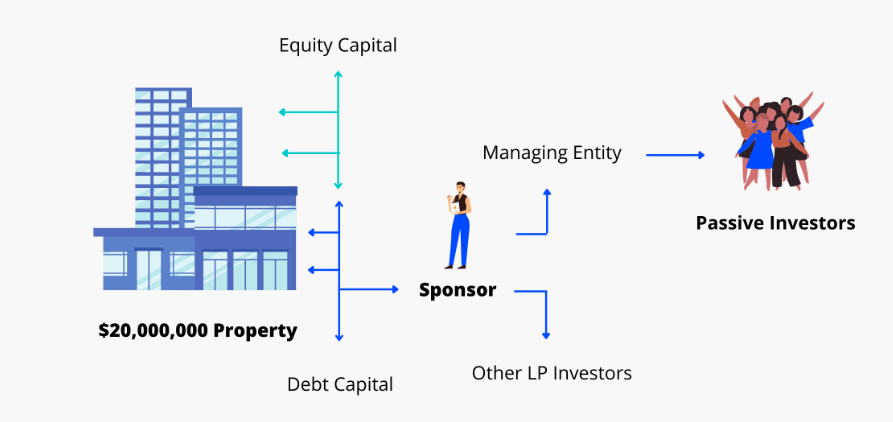
The Synergy of General and Limited Partnerships
At the heart of a real estate syndication is the synergy between two groups: the General Partners (GPs) and the Limited Partners (LPs). The GPs are the strategists and managers, steering the ship with their expertise in property management, while the LPs contribute financially without the hassle of day-to-day management. This structure allows you to invest passively, reaping the benefits of real estate without the typical burdens of property ownership.
The Power of a Limited Liability Company (LLC)
By forming an LLC, both GPs and LPs create a robust framework for holding and managing the property. This legal structure not only streamlines the investment process but also offers you protection and peace of mind.
Consistent Returns and Financial Growth
One of the most attractive aspects of multifamily syndication is the potential for consistent, quarterly cash flow distributions. As a passive investor, you can enjoy a steady stream of income while the property appreciates in value under the expert management of the GPs.
The Final Flourish: Sale and Profit Sharing
The journey culminates with the strategic sale of the property. After enhancing its value and achieving the investment objectives, the property is sold. This is where you, as an investor, see the fruition of your investment – the return of your initial capital and a share in the profits.
Related Investing in Multifamily: A Manual for 2024
Why Multifamily Syndication Stands Out
1. Access to Bigger Deals: Step into the realm of significant commercial properties.
2. Diversification: Spread your investments, reducing risk.
3. Ease of Investment: Share responsibilities, focusing on what you do best.
4. Tax Advantages: Leverage tax benefits to maximize your returns.
Multifamily real estate syndication is more than just an investment; it’s a journey towards financial growth, a pathway to diversify your portfolio, and an opportunity to be part of something bigger. Ready to unlock the door to your real estate investing future? Join the world of multifamily syndication and watch your investment dreams turn into reality.
